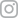
Hyperpigmentation refers to dark patches of skin that develop with age. It’s a common condition that can affect many people for different reasons. Usually caused by sun exposure, skin inflammation, adverse reactions to drugs, medical conditions like Addison’s disease, and hemochromatosis, hyperpigmentation occurs when the skin produces more melanin than in surrounding areas. It’s a common skin condition that affects all skin types and most commonly occurs on the face, arms, back of the hands, and legs. Although the condition is generally harmless, it can sometimes point to another medical condition.
There are different types of hyperpigmentation, with the most common ones being:
- Age spots – Also known as liver spots, these are dark spots that most commonly appear on the face and hands in older adults, especially after sun exposure.
- Melasma – Large patches of dark skin, also known as chloasma or “the mask of pregnancy,” usually appears on the face, stomach, and forehead of pregnant women or those taking birth control pills.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation – Dark skin patches like acne or eczema on the face or neck may appear after an inflammatory skin condition or a skin injury.
Treatment
A few home remedies can help reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation, including licorice, aloe vera, or green tea. By staying out of the sun, wearing sunscreen daily, and avoiding picking at the skin (on spots, scabs, and acne), you can prevent the condition from worsening or forming in the first place.
If you have hyperpigmentation and want to get rid of it, a dermatologist can help you identify the type and cause by taking a small skin sample (biopsy) and then recommending the optimal treatment plan for you. However, melasma can usually be diagnosed just by looking at your skin. It generally takes between 6-12 months for dark spots to fade, and even longer if the dark pigment goes deep into the skin. Depending on your goals and budget, an at-home treatment or cosmetic procedure may help accelerate that process. Your options include:
- Topical creams – Corticosteroids, azelaic acid, vitamin C, kojic acid, or retinoids may help to treat the condition and brighten the skin.
- Cosmetic procedures – Chemical peels, laser therapy, microdermabrasion, and intense pulsed light may lighten the skin and reduce hyperpigmentation. These procedures are more expensive than over-the-counter medication and skincare products and may require some downtime afterward. However, you can expect to see significant results faster and enjoy them longer.